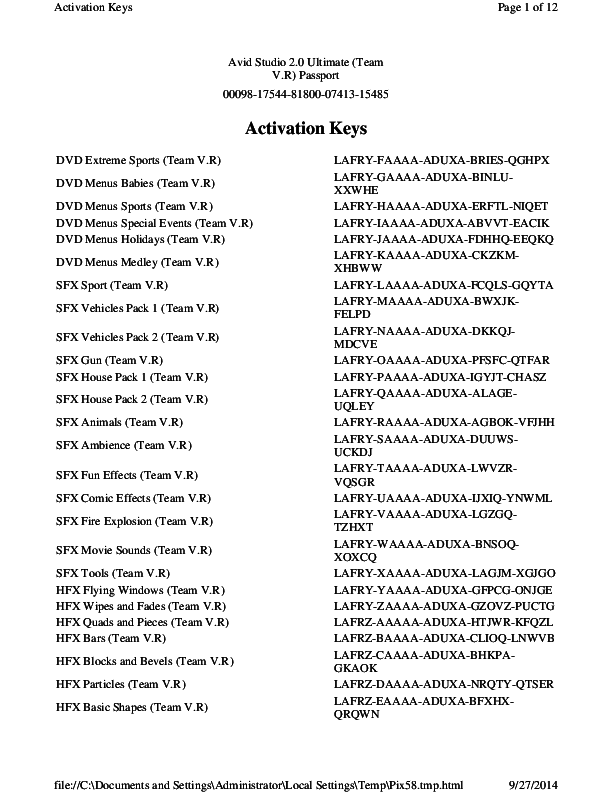
This may resolve your issue, if the problem persists, proceed to Step 2. Step 2 - Regenerate Activation Keys: If the content is listed in Studio 14, but it is locked, try to unlock the content. Within Studio go to Help - Regenerate Activation Keys. This will unlock installed content that we have associated with your purchases. Jun 11, 2021 Update: - RTFX expansion v.2.0 - Over 500 brand-new aspects - New tutorials Update: - 60 brand-new aspects - 20 message computer animations Update: - RTFX expansion v.1.0 - 440 aspects GEBRUIKTE MATERIALEN. Sommige materialen in de promovideo zijn gelicentieerd onder een Imaginative Commons BY. Pinnacle RTFX Volume 2 Pinnacle RTFX Volume 2. KASPERSKY 2011 11.0.1.400 ACTIVATION TRICK USING KEY FILES! This article shows the comparison between Studio 14 HD, Studio 14 Ultimate, and Studio 14 Ultimate Collection. Pinnacle Studio Ultimate Collection (14) Pinnacle Studio Ultimate (14) Pinnacle Studio HD (14) Activations. Activation Keys. Activation Keys Page 1 of 12 Avid Studio 2.0 Ultimate (Team V.R) Passport 4-3-15485 Activation Keys DVD Extreme Sports (Team V.R) LAFRY-FAAAA-ADUXA-BRIES-QGHPX LAFRY-GAAAA-ADUXA-BINLU- DVD Menus Babies (Team V.R) XXWHE DVD Menus Sports (Team V.R) LAFRY-HAAAA-ADUXA-ERFTL-NIQET DVD Menus Special Events (Team V.
MTM is the abbreviation of Methods- Time Measurement. Methods-Time Measurement means that the time required to perform a specific task depends on the method chosen for the activity. The MTM method was developed in the USA in the 1940s as a system of predetermined times and was published in the book “Methods-Time Measurement” in 1948. Since that time, MTM has been used both as an analytical tool for directly analyzing manual work processes, as well as, a tool for developing standardized building blocks from the MTM basic system (MTM-1). These building blocks are being used to economically describe, quantify and design a wide range of work processes. Compared to other systems of predetermined times, MTM enjoys the greatest worldwide distribution as an instrument of industrial engineering and time management. In addition, building block systems were developed based on MTM-1 for application in different process types (mass production, batch production and one-of-a-kind and small variable batch production).
The traditional time study*, or the. Times Systems such as MTM-3 reduce the required observation time yet maintain the usefulness of the estimates. Time and Motion study D.S.S.C.P.Subasinghe. MTM Ex: MTM --19651965. Time & Motion Study.ppt [Compatibility Mode]. MTM-1: Methods-Time Measurement. The MTM Association also offers a course to teach users of the TiCon Base how to effectively implement the software system for.
MTM offers a worldwide uniform standard for businesses to use in describing and quantifying manual work pro-cesses. As early as the 1990s, MTM began the gradual transformation from a system of predetermined times to a productivity management system.
Today, the MTM method includes a framework of MTM building block systems used to model the full range of work processes. MTM supports the design of work processes (business processes) through describing, structuring, planning and analyzing/synthesizing, using process building blocks designed for content and time. MTM systematically classifies and organizes processes, while making the Influencing Factors that control them transparent, thus achieving the goal of “First Time Right” in the design of work systems. An essential goal of a company consists of maintaining and increasing competitiveness. A system of comprehensive data and time management linked throughout every level of a company’s operation is an indispensable instrument of productivity management in reaching this goal.
By designing its processes according to the principles of the First Time Right, it is possible for a company to create work systems that precisely meet its objectives from their inception. Using these concepts, a production system can be developed as a Best-Practice solution. MTM is taught and used both as a tool in the truest sense, as well as, a method or principle in the broader sense. Within a production system, MTM serves the function of a common language providing a standard for design, as well as, serving as the basis for measurements, comparisons and modifications made at all levels of this system. However, the roll of the employee changes, such that he or she now joins the specialist in taking responsibility for improving the work processes.
Communication with the involved employees becomes a central principle. Workshops, presentation techniques, problem solving in teams, visualization and mutual determination of performance characterize the new method of manufacturing. The following table demonstrates the suitability of various time determination methods for meeting the primary needs characterized in the new method of manufacturing. Thus, MTM proves to be the premier work measurement tool for use in the new method of working, showing itself to be a suitable instrument for integrated use in all the individual phases of the value added chain. The use of MTM starts at the very beginning of the value added chain. Its influence begins with the product idea and continues through all of the successive stages of design, production, repair and maintenance, making it a vital constant all the way to the end of the product life cycle. “ First Time Right!” is a guiding principle emphasizing the importance of optimizing costs and productivity during the product development stage of the value added chain.
Along the value added chain, the use of MTM and Lean in a coordinated manner proves to offer the optimum opportunity to avoid waste. MTM and Lean philosophies are used to analyze all processes in a company with respect to their value added contribution and to improve them, if required. In doing so, staff, products and the production processes achieve maximum harmony. The target contributions of MTM and Lean can be described as follows.
MTM based on local optimization of activities To use MTM and Lean together, along the value added chain, means to make the optimum use of both the synchronization of the value stream and methods design, in order to ensure low-waste flow coupled with efficient work methods! MTM supports the entire value added chain of a company and runs in two phases within the management of work systems. In the first phase ( The MTM Planning Concept – illustrated below) economic and human (ergonomic) aspects of planning the work system are given highest priority. The goal is to achieve a Best-Practice level of productivity, validated by benchmarks, at the very beginning of production. The planning concept shown above has proven itself within the core phases of design, planning and production, lending primary importance to the interdisciplinary cooperation (simultaneous engineering) required of the changing partners of each phase, including production employees, in the design of the value added chain.
The best opportunities for cost-saving are found in the design and planning phases. ProKon ( Produktionsgerechte Konstruktion – Production-Oriented Design) proves itself as a premier MTM tool for assisting the designer in creating assembly-friendly products while allowing quantification of savings in the product development phases. The MTM Planning Concept is used to structure processes and divide the workload between people and machines. MTM analyses serve as the basis for comparing work methods and selecting the best among them. The MTM planning analyses for the selected work methods determine the corresponding work system design.
They provide the basic data used for calculating production times and for balancing the production process. Employees should be introduced to and familiar with the planned work system by the start of production.
The second phase ( The MTM Optimization Concept) covers the operational phase of the work systems following the start of production (SOP). Here, the focus is placed on continuous improvement by operators, supported by an accurate results analysis. When a consistent data concept is applied and appropriate methods and tools are used, the combining of MTM and Lean in both phases allows for the reduction of waste in flow and method (see the illustration below). Legend: COE Change-Over Efficiency MAST Manual Abilities Scanning Test TPM Total Productive Maintenance PDCA Plan – Do – Check – Act MSA Multi-Place Operations CIP Continuous Improvement Process VSD Value Stream Design VSM Value Stream Mapping Sankey-Diagram specific type of flow diagram, in which the width of the arrows is shown proportionally to the flow quantity By the combined utilization of Lean and MTM philosophies, optimal productivity is achieved in significantly less time. Even after the start of production, there is a more significant increase in productivity when MTM is being applied, because MTM enables the user to accurately analyze and realize the true benefits of identified potentials.
A work system description is necessary to allow this process to move forward. It contains building blocks of data representing both the spatial dimensions in the work system (e.g., with the use of diagrams or photos) and the variables of the work system. Fiat: ERGO-UAS system 'The introduction of the ERGO-UAS system has dramatically changed the way of developing the new products and of managing Production and the Industrial Relations.

No motion can be designed, implemented and executed in our company without the scientific assessment of the biomechanical load generated by the motion itself. The paradigm 'more productivity less health' has been turned into the new 'more productivity more health' and the ERGO-UAS system has become one of the fundamental pillar of our production system' Luigi Gennaro Galante, VP Manufacturing EMEA, Fiat Group Automobiles SpA.
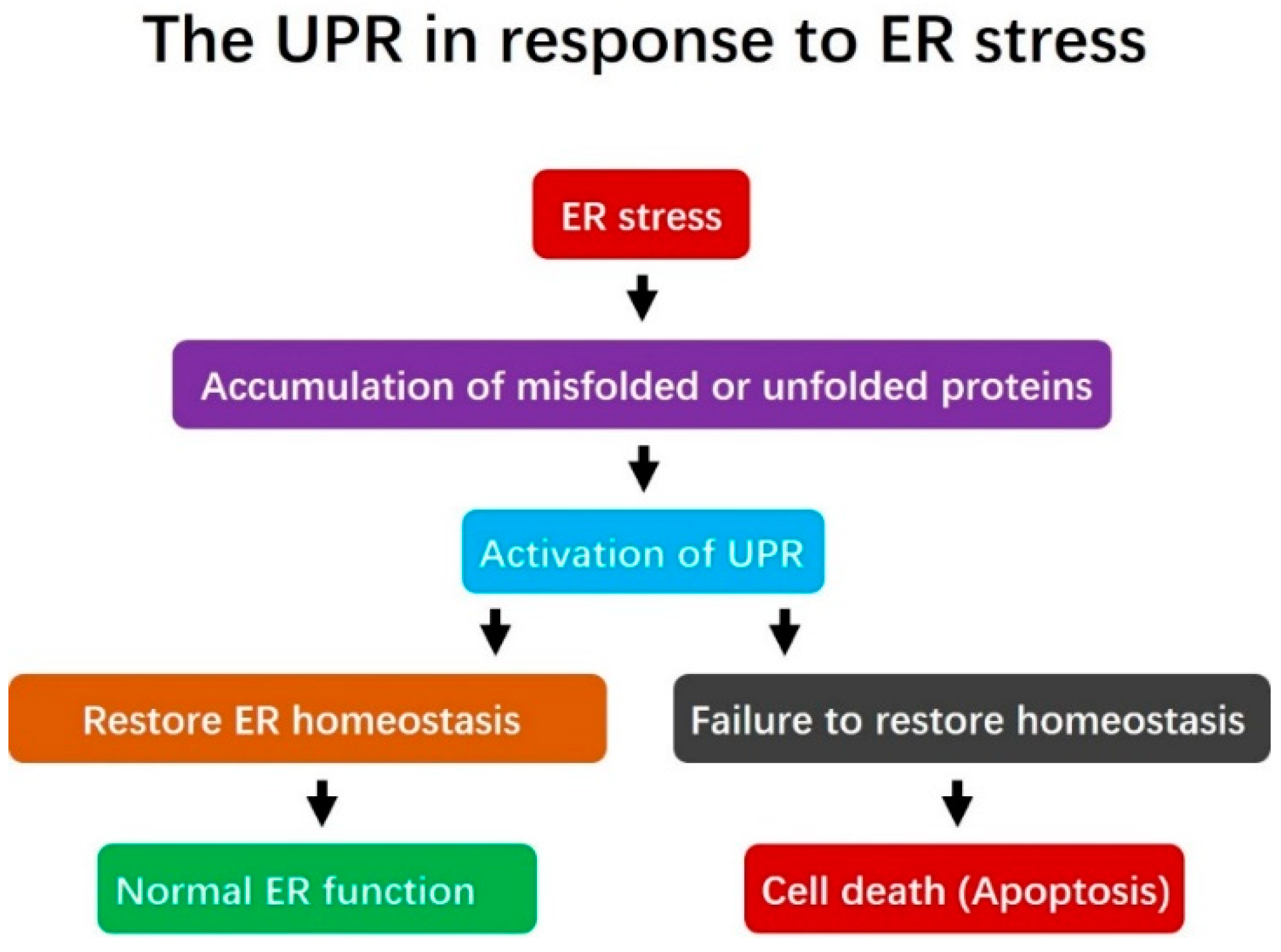
This article includes a, but its sources remain unclear because it has insufficient. Please help to this article by more precise citations. (March 2014) A predetermined motion time system (PMTS) is frequently used to perform Labor Minute Costing in order to set piece-rates or wage-rates in labor (labor) oriented industry by quantifying the amount of time required to perform specific tasks.
One of the most popular authors of all time, V.C. Andrews has been a bestselling phenomenon since the publication of Flowers in the Attic, first in the renowned. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Download crack or serial for. Andrews Collection ePub eBooks. Full Download V.C. Andrews Collection ePub eBooks. Buy online - V.C. Andrews Collection ePub eBooks. Vc andrews ebook collection.
One of such a system is known as, released in 1948 and today existing in several variations, commonly known as MTM-1, MTM-2, MTM-UAS, MTM-MEK and MTM-B. Obsolete MTM standards include MTM-3 and MMMM (4M). The MTM-2 standard has also largely been phased out by the organization, but is still used in some commercial applications.
Predetermined Motion Time Standard and Predetermined Time standards (PTS), Pre-determined Time Systems are other terms that describe same concept by different authors. PMTS commonly presented in term of SMV (Standard Minute Value)/ SAM (Stranded Allocated Minute). Contents. APD- Apparel Production Data APD- Singapore origin web based software platform to determine SMV, SAM of the Cutting, Sewing, Packing of the Garment, Footwear, Bag manufacturing production units. Apparel Production Data which is a tool to help to factory production to increase their productivity and efficiency by identifying waste motions specially in this very challenging market.
All production operators can be analysis the SAM / SMV to accomplished their job task. Operation database will indicate all the step by steps to complete a garment. APD allows user to customize the ADD parameter such as machinery allowance, Fabric type, Stitch per centimeter etc. APD is MTMII based analytic followed by ILO stranded protocols for work-study for personal fatigue, environment rating, contingency allowance etc Module Feature. SAM and SMV can helping factory to increase productivity and to eliminate unnecessary process. To Increase workers efficiency. To Improve Factory efficiency and also categories of product line.

To reduce production cost. To preventive any losses of happens during production activities. Other Features Structure by web-based Generate two types of reports to Portable Document Format, Excel (.xlsx) All export document processing is required only two tools browser and third party reader (like Adobe Reader, Microsoft Excel). Mobile, PC based Video streaming for accurate communication of the methodology via web. Security Users can be defined with access to only certain options using a role based model. Functions which they do not have access to will not be shown. User permission can be authorized to control and limited to some of the categorized and others locations.
Main menu is present by the user permission authority, it make some of the options will not provide to the main screen to allow user to access it. MOST Another popular PMTS is the, which was first released in 1972. Was acquired by in 2007. That method also has several variations, with the most commonly used being BasicMOST, and others being MiniMOST, MaxiMOST, and AdminMOST.
The variations of both systems differ from each other based on their level of focus. MTM-1 and MiniMOST are optimal for short processes with only small hand motions.
BasicMOST, MODAPTS and MTM-UAS are more suitable for processes that average around 1 to 5 minutes, while MTM-B and MaxiMOST are more properly used for longer processes that are less repetitive. MODAPTS Yet another popular PMTS used today in the automotive, sewing and healthcare industries is the MODAPTS technique. This technique was introduced in 1966 by who originally learned the MTM-1 and MTM-2 methods in the 1950s and sought a simpler technique to use and apply. Unlike the MTM and MOST standards, MODAPTS uses a MOD as its basic unit of measurement (1 MOD = 0.129 seconds). However, like Basic-MOST, MODAPTS uses a coding technique that consists of a letter and an integer number (all but 1 code), where the integer numbers each represent MODS that can be easily added to determine a coded task's time. MODSEW MODSEW is a software application of MODAPTS for the sewn products and apparel industries. It uses very intuitive codes to represent the various motion patterns prevalent in the industry and allows the user to configure their own codes for those unique to their operation.
The software is used to determine the standard time to complete an operation and has provisions to collect and maintain groups of operations in a style (product). MODSEW is owned, maintained, sold and supported by Byte Software Services, LLC of Mauldin South Carolina. Coats GSD General Sewing Data is a PMTS for the sewn products and apparel industries and is based on MTM Core Data both proprietary data systems of GSD (Corporate) Ltd of Preston, UK. The Time standards for General Sewing Data are used in GSD Enterprise and GSD QUEST. GSD company was taken over by thread giant Coats in 2015. Pro SMV Pro SMV is another PMTS for the sewn product industry, offered by Methods Apparel Consultancy India Private ltd. As an individual module of their software series pack called Pro-Suite.
Pro Suite is aimed at providing various IT solutions for various departments of Sewn product industry. It has made a very strong consumer base in India and neighboring countries. SATRA TimeLine SATRA TimeLine accurately predicts the time and labour costs of a footwear production line before production starts. At its core is a Predetermined Motion Time System ( PMTS), that can calculate values for every single shoemaking operation based on industry accepted standards and SATRA’s vast experience and knowledge. This innovative system is offered by SATRA Tecknology Centre (UK).
SATRA TimeLine is a unique production efficiency system, designed BY shoemakers FOR shoemakers and it is exclusively available to SATRA members. SewEasy GSD. is a more recent garment sewing data (GSD) system used by Fortune 500 apparel brands, sourcing companies and sector manufacturers alike in Ready Made Garment (RMG) supply chain capacity plan accuracy management. Seweasy is more aligned with the lean concepts attributed to.
This system focuses on providing Standard Minute Values (SMV), which is also known as Standard Allowed Minutes (SAM) quickly for labour cost estimation in sewing. The living wage and escalating costs, 'demand innovations and smooth work flow' in manufacturing location, to stay competitive and sustainable. The company provide free training on-site.
The. transparent garment sewing data is useful for “sewing load balancing' in line with (VSM) and 'added value' measurement known as 'needle down time' among professionals. has trained many juniors and seniors alike, to quickly establish standards using this easy PMTS system. The process of.
based sewing standardization leads to easier skills development and worker empowerment useful in performing innovations at needle point. The Cost Engineering aspect is important for Living Wage bench-marking and incentive systems development for motivation. Open Costing for Garment Sourcing Teams Recent research by Manchester University, UK on Garment Labor Costs and demand for living-wage benchmark brought. open, transparent, quick garment sewing data and (MTM) to the notice of apparel industry's sourcing professionals, including Walmart, who adopted.
to create a sustainable labour-costing model for sourcing garments and home textiles in 2013. This approach is explained by ASDA in Clean Clothes Campaign annual report too. Home Textiles, Shoes, Leather, & Upholstery. can be used in all needle based sewing industries such as Home Textiles, shoe, leather, and upholstery; where piece rate rationalization, open costing and living wage focus are under way.
SewEasy GSD Lean approach for Muda, Mura and Muri Unlike 'time studies', in which an analyst uses a stopwatch and subjectively rates the operator's effort to calculate a standard time, Seweasy PMTS requires that the analyst break apart the process into its elemental sewing actions, and add-up the times to calculate the total standard time. Process of estimating cost of labour and workflow, professionally in such manner leads to improved productivity, lowered cost and higher earnings for all stake holders by way of eliminating wastes Muda, Mura and Muri. TMU Most predetermined motion time systems (MTM and MOST) use time measurement units (TMU) instead of seconds for measuring time. One TMU is defined to be 0.00001, or 0.036.
These smaller units allow for more accurate calculations without the use of decimals. In the most in-depth PMT systems, motions observed will be on the level of individual TMUs, like toss (3 TMUs in MiniMOST) and simple pick-up (2 TMUs in MTM-1). More general systems simplify things by grouping individual elements, and thus have larger time values – for example, a bend and arise (61 TMUs in MTM-2) and one or two steps (30 TMUs in BasicMOST). Systems with even less detail work with TMU values in the hundreds, like climbing 10 rungs on a ladder (300 TMUs in MaxiMOST) or passing through a door (100 TMUs in MaxiMOST). The choice of which variation of a certain PMTS to use is dependent on the need for accuracy in contrast to the need for quick analysis, as well as the length of the operation, the distances involved in the operation, and the repetitiveness of the operation. Longer operations often take place on a larger spatial scale, and tend to be less repetitive, so these issues are often treated as one. For longer, less repetitive operations, statistical analysis demonstrates that the accuracy of less detailed systems will generally approach the accuracy of more detailed systems.
Thus, in order to reduce the time required for analysis, less detailed systems (like MTM-B and MaxiMOST) are usually used when possible. Conversely, very short, repetitive processes are commonly analyzed with more exact methods like MTM-1 and MiniMOST because of the need for accuracy. ILO & Manchester University research during 2009 to 2013 Manchester University researchers including Doug Miller, has gone deep into uses of PMTS in apparel labour costing in 'Towards Sustainable Labour Costing in UK Fashion Retail.' Doug says.work measurement for arriving at a standard time should normally make provision for relaxation, contingency and special allowances. According to the International Labour Organization (ILO), as of 1992 there were some 200 different PTS systems. In apparel manufacture, three PTS consultancy firms specializing in MTM appear to be operating in the sector– the US-based MODAPTS, the Sri Lankan-based and the UK-headquartered GSD (Corporate) Ltd. Link to Doug's article is provided below in References.
Rtfx Volume 2 Activation Keys
Comparison of PMTS systems by Walmart Walmart has launched in house PMTS system under lean cost reduction program across Asia. A review appear here: See also Closely related manufacturing improvement methodologies:. Modern Concepts and related Terminology:. Sustainable Labour Costing in Apparel:. Labour Minute Costing: A TOOL FOR ESTABLISHING LIVING WAGE Notes.
Mtm Time Study Excel Template
Kanawaty, G. Introduction to Work Study, International Labour Office, 1992,. Miller, Doug, Towards Sustainable Labour Costing in UK Fashion Retail (February 5, 2013). Available at SSRN:: References.
Rtfx Volume 2 Activation Product
Mtm Time Standards
Rtfx Volume 2 Activation Key
Zandin, Kjell B (2003). MOST Work Measurement Systems.: Marcel Dekker. Miller, Doug, Towards Sustainable Labour Costing in UK Fashion Retail (February 5, 2013). Available at SSRN::. External links. Methods Workshop (ETC) Estimated True Cost. What is Standard Time by Coats GSD.